TUBB3
TUBB3
Tubulin beta-3 (TUBB3)
TUBB3 is a beta-tubulin gene. It is active in mature neurons and TUBB3 mutations are thought to affect later stages of brain development such as neuronal maturation and connectivity.
To date, there have been over 30 different TUBB3 mutations described in the literature to date.
For the most part, individuals carrying TUBB3 present with two distinct features: 1) brain malformations (e.g. polymicrogyria) or 2) normal brain structure but with problems of the muscles surrounding the eye muscles, called Congenital Fibrosis of the Extra-Ocular Muscle 3 (CFEOM3). CFEOM3 causes ptosis (drooping eye lids) and restricted eye movements.
Recently, a small number of children presenting with both brain malformations and CFEOM3 have been identified.
Unlike some other Tubulinopathy genes, TUBB3 mutations are a mixture of familial and de novo (not inherited from a parent) mutations.
Multiple individuals carrying TUBB3 E410K variants have been reported to share a distinct disease state; in addition to CFEOM3, this includes Kallmann Syndrome, facial weakness, progressive peripheral neuropathy, vocal cord paralysis and cyclic vomiting.
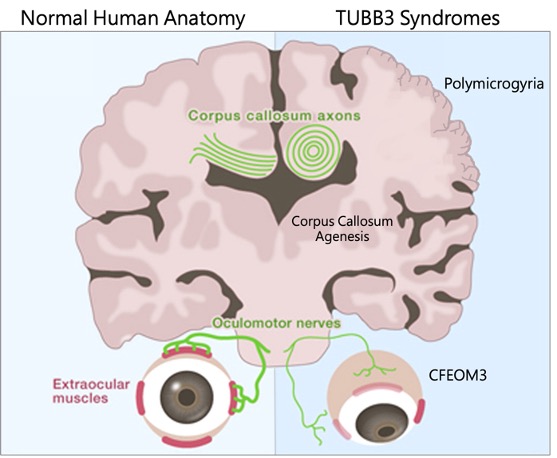
Variants affecting TUBB3 are commonly associated with i) brain surface malformations (e.g., polymicrogyria); ii) congenital fibrosis of the extra-ocular muscle type 3; and iii) abnormalities of the corpus callosum, a large bundle of neuronal fibres connecting the two brain hemispheres. Image adapted from Tischfield et al., 2009.
