TUBB2B
TUBB2B
Tubulin beta-2B (TUBB2B)
TUBB2B is a beta-tubulin gene which is active in progenitor (neuron-producing) cells and neurons during brain development. After birth, its expression switches to a type of neuron-supporting cells, called macroglia.
To date, there have been over 40 different variants identified in TUBB2B. Mutations in TUBB2B are commonly associated with polymicrogyria, a malformation characterised by abnormally small and bumpy folds on the surface of the brain (see image, right). The way in which TUBB2B malformations cause polymicrogyria is still not fully understood.
Other brain malformations have also been linked with TUBB2B mutations however, including simplified brain folding, lissencephaly, microcephaly and schizencephaly.
A number of individuals carrying TUBB2B E421K variants have problems of the muscles surrounding the eye muscles, called Congenital Fibrosis of the Extra-Ocular Muscle 3 (CFEOM3), which is commonly associated with TUBB3 mutations.
Familial TUBB2B R390Q mutations have also been identified in three related individuals presenting with quadrupedal locomotion (walking on all fours), with MRI scans highlighting an underdevelopment of the cerebellum, an important part of the brain for motor co-ordination.
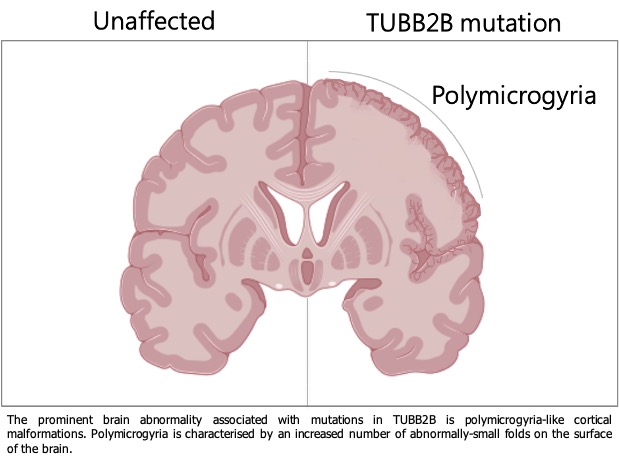
The prominent brain abnormality associated with mutations in TUBB2B is polymicrogyria-like cortical malformations. Polymicrogyria is characterised by an increased number of abnormally-small folds on the surface of the brain.
